|
Micropolar effect on the cataclastic flow and brittle-ductile transition in high porosity rocks
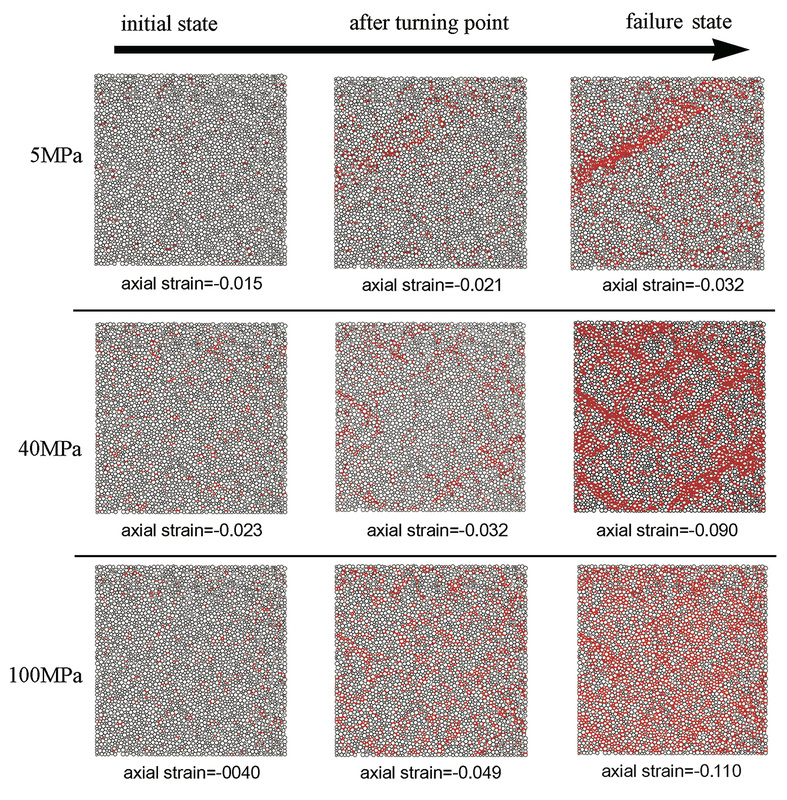
A micro-mechanical DEM model is adopted to analyze the grain-scale mechanism that leads to the brittle-ductile transition in cohesive-frictional materials. The cohesive-frictional materials are idealized as a particulate assemblies of circular disks. While the frictional sliding of disks is sensitive to the normal compressive stress exerted on contacts, normal force can be both caused by interpenetration and long-range cohesive bonding between two particles. Our numerical simulations indicate that the proposed DEM models is able to replicate the gradual shift of porosity change from dilation to compaction, and failure pattern from localized failures to cataclastic flowupon rising confining pressure in 2D biaxial tests. More importantly, the micropolar effect is examined by tracking couple stress and micro-crack initiation to interpret the transition mechanism. Numerical results indicate that the first invariant of the couple stress remains small for specimen sheared under low confining pressure but increases rapidly when subjected to higher confining pressure. The micropolar responses inferred from DEM simulations reveal that micro-cracking may occur in a more diffuse and stable manner when the macroscopic couple stress are of higher magnitudes.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Group NewsNews about Computational Poromechanics lab at Columbia University. Categories
All
Archives
July 2023
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed